Everything you need to know about capital gains

In Australia when you sell certain assets, such as an investment property, you could become liable to pay CGT. For the purposes of this article, and in the context of this site, we are going to assume your investment is a property. Any profit, or gain, you receive from the sale of an investment property will be assessable as part of your annual income tax assessment.
This article will help you understand:
- What exactly CGT is
- When CGT applies
- Exceptions and exemptions from CGT
- How you can avoid or minimise CGT
- Self managed super funds (SMSF) and CGT
- How to work out your CGT
What is Capital Gains Tax or CGT?
So what is Capital Gains Tax (CGT)? CGT is a tax on the profit you get from the sale of an investment, such as a rental property or even a plot of land. It also applies if you give away an asset to someone else.
Even though it is referred to as capital gains tax it is not a separate tax, and is part of your annual income tax assessment. You can also make a capital loss, if for example you sell an asset for less than what it initially cost you.
"Capital gains tax it is not a separate tax, and is part of your annual income tax assessment CGT and your primary residence"
CGT does not generally apply to the home, or dwelling, you live in. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) defines a dwelling as, ‘anything that is used wholly or mainly for residential accommodation’. Your primary residence includes a property where:
- your mail is delivered
- you are registered on the electoral roll
- all your personal belongings are kept
There is no minimum time before a property is considered your main residence, but the longer you live there the more likely it will qualify in the eyes of the ATO.
Read: Real estate terminology explained
When does Capital Gains Tax apply?
CGT generally applies to any kind of property that is not classed as your primary residence, including houses, apartments, and commercial or industrial premises. As an Australian resident, CGT also applies to any assets you own elsewhere in the world. It is assessed in the tax year that the transaction, the sale of your investment property or asset, took place.
"Capital gains tax generally applies to any kind of property that is not classed as your primary residence"
What is exempt from CGT?
The most significant exemption to CGT in Australia is your main residence or family home.
Other assets that are exempt from this tax include personal assets such as your car, some collectables and personal use items purchased for less than $10,000. Any assets acquired before CGT came into effect, on 20 September 1985, are also exempt.
How you can minimise or avoid paying Capital Gains Tax
The most obvious way of avoiding CGT is to hold onto your investment property. You only incur CGT when you sell an asset. You could also live in the property, and make it your primary place of residence, which is exempt from CGT. If you move out of your home and rent it out, you may be exempt from some CGT. This is because the law allows you to treat your home as your primary residence for up to six years.
"You only incur capital gains tax when you sell an asset, such as an investment property"
Holding the investment for longer than a year also helps by reducing capital gains tax by 50 per cent. Also remember to record all the expenses you have incurred managing or improving it. These can help reduce your tax liability when it is sold. You can also reduce your tax liability by buying a property through your self managed super fund (SMSF), but you need to meet certain criteria, including having a SMSF balance of $120,000 or more.
"You can reduce your tax liability by buying a property through your self managed super fund (SMSF)"
Read: How will the new investor/owner-occupier rate changes affect the property market?

Self-managed super fund (SMSF) and CGT
There are a number of tax saving benefits to buying property via your SMSF. These include avoiding CGT, and having any rental income taxed at the comparatively low rate of 15 per cent. And if you've owned the property for more than 12 months, you may also be able to limit the CGT your SMSF pays to 10 per cent. If you are considering setting up a SMSF, or purchasing a property in your fund you should seek the appropriate advice, as the rules around establishing and running them are complex.

Calculating your CGT
There are a few different methods to calculate your capital gains tax:
Capital gains tax discount
If you hold any capital gains tax asset for longer than 12 months you will get a 50 per cent discount on your capital gain. If you sell your asset in less than 12 months you pay the full capital gain.
Indexation
This method is for any assets purchased prior to 21 September 1999, and which you have held for 12 months or longer.
Capital loss
If you have made a loss from the sale of an asset, such as an investment property, you can use it to reduce the tax from other capital gains.
Working out your capital gain or loss
The easiest way to work out the capital gains tax you are liable for, is to take the selling price and subtract the original cost and any associated expenses you have incurred. The remaining amount is your capital gain.
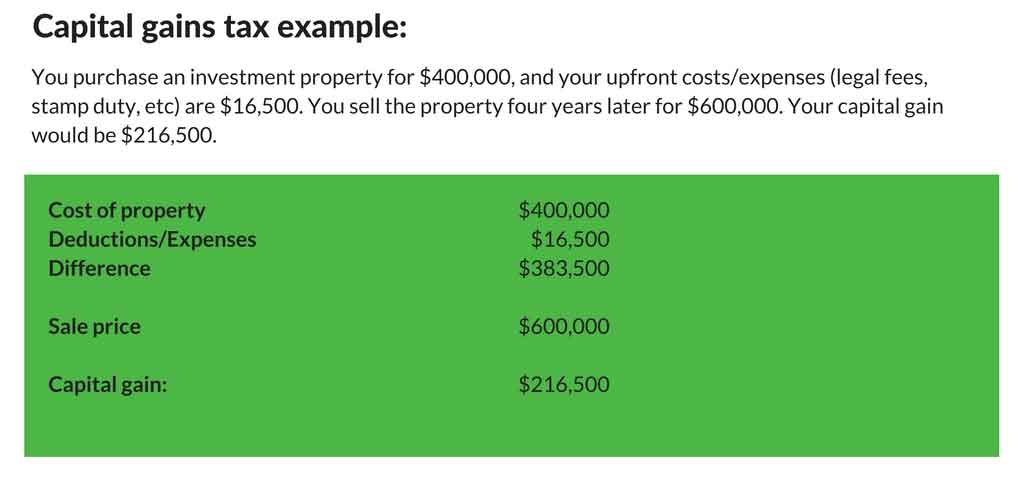
If you make a net capital loss in an income year, you should not be liable to pay CGT. However, you cannot offset this against your other income. It needs to be offset against any capital gains you incur in future tax years.
"If you make a net capital loss in an income year, you should not be liable to pay capital gains tax"

*Capital gains tax is complex and individual circumstances vary. We advise you to seek legal and financial advice from the appropriate professionals. You can also visit the Australian Taxation Office for more background on capital gains tax. Working out if you made a capital gain (or loss) in an income year is easier if you keep detailed records. This includes valuations of a property, sale contracts, and receipts of all expenses related to your investment.